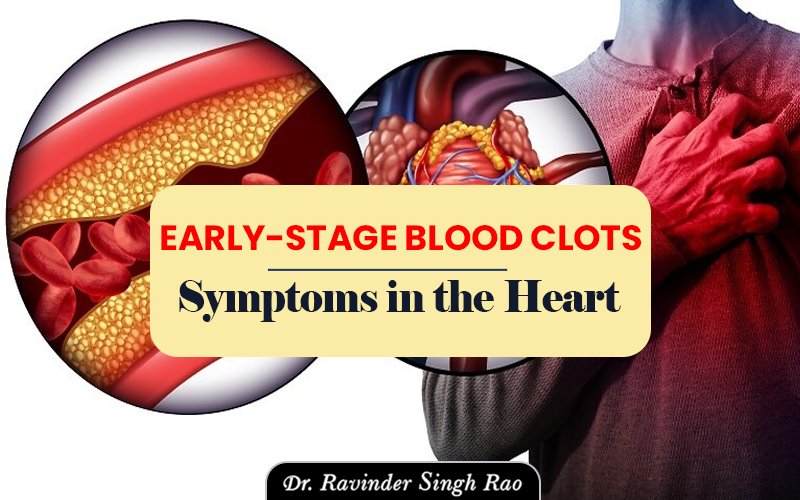
Blood clots can form in the body’s veins or arteries, which is a potentially deadly condition. Despite being a normal reaction to trauma, blood clots can have fatal consequences if they develop in vital organs like the heart, lungs, or brain. For example, blood clots in the heart can result in cardiac arrest and even heart failure. People can take the right actions to prevent or manage blood clots by being aware of the signs and hazards associated with the illness. If you are diagnosed early, you have more time to see a cardiac specialist and receive the required care. Cardiac thrombosis, another name for early-stage blood clots in the heart, may not necessarily have obvious symptoms at first, but more subtle indicators may point to a possible danger. You may experience unexplained pressure, chest discomfort, or pain that feels like heaviness, along with shortness of breath even during mild activities.
Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao, an expert cardiologist in Jaipur, explains that early-stage clots in the heart often come with precise warning signs. Particularly when you’re worried or active, you may experience a slight heaviness or pressure in your chest. You may also notice being unusually short of breath, even with small tasks, or feeling extra tired for no obvious reason. Your heart may speed, skip a beat, or beat irregularly at times. Although these symptoms might not seem like much, they can cause major issues, such as a heart attack, if they are neglected. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao emphasizes that in order to prevent a clot from spreading or becoming harmful, even little or infrequent warning signs should be promptly treated.
Heart Doctor, TAVI Surgery, TAVI Procedure, Best Cardiologist, TAVI Cardiologist In India, TAVR Cardiologist in India
TAVI Expert in Jaipur – Cardiologist Expert in Jaipur – Heart Specialist Doctor in Jaipur
Risk Factors of Blood Clots
The risk of a blood clot can be raised by a number of circumstances. Among the most prevalent risk factors are:
- Age: People are more vulnerable to blood clots as they get older.
- Family History: Blood clots are more likely to occur in people who have a family history of the disorder.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: The risk of blood clots might be increased by prolonged inactivity, such as prolonged sitting.
- Obesity: Obesity and excess weight can raise the risk of blood clots.
- Smoking: Smoking can harm blood vessel linings, increasing the risk of blood clots.
- Medical Conditions: Blood clots can occur as a result of certain medical diseases, including diabetes, cancer, and heart disease.
- Medications: Blood clots can be caused by some drugs, including hormone replacement treatment and birth control pills.
- Surgery: Surgery, especially if it involves the legs or pelvis, can increase the risk of blood clots.
Different Body Parts Where Blood Clots Can Form
Although blood clots can occur anywhere on the body, they most frequently occur in the deep veins (a disease called deep vein thrombosis). Other areas where blood clots can form include:
- Lungs: When a blood clot makes its way to the lungs, it can result in pulmonary embolism, a potentially fatal illness.
- Brain: A stroke brought on by blood clots accumulating in the brain can result in permanent impairment or even death.
- Heart: Heart attacks can be brought on by blood clots that develop in the coronary arteries.
- Abdomen: A serious illness known as mesenteric thrombosis can result from blood clots in the mesenteric arteries, which carry blood to the intestines.
- Arms: A disorder known as thrombophlebitis can result from blood clots forming in the arm veins.
Blood Clots in the Heart: A Closer Look
A heart attack may result from a blood clot in the heart that prevents blood from reaching the heart’s muscles. For the heart muscle to work effectively, oxygen-rich blood must be continuously supplied. The heart muscle can suffer damage or perhaps perish if that is disrupted. The size and location of the blood clot, as well as the length of time it takes to treat heart disease, determine how much damage has been done.
Serious consequences, such as irregular heartbeats or heart failure, may result from delaying treatment from a heart disease specialist. In some cases, a pulmonary embolism or stroke could result from the blood clot breaking loose and moving to other areas of the body.
Signs of Blood Clots in the Heart
It’s essential to identify the early signs of a cardiac blood clot and get medical help right away if you experience them, because of the terrible outcomes covered in the preceding section. Serious problems can be avoided, and results can be improved with early diagnosis and treatment. Treatment for a heart clot may include surgery to remove the clot, medications to dissolve or prevent blood clots, or surgery to restore blood flow to the heart muscle. To ensure adequate blood flow to the heart’s chambers, angioplasty may occasionally be necessary.
Early-stage blood clot symptoms in the heart can include;
- Sweating
- Pain or discomfort in the chest that could feel like a squeeze or pressure
- Shortness of breath
- Pain that radiates to the back, neck, jaw, shoulders, or arms
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or weakness
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
Keep in mind that different people have different heart attack symptoms. Some folks might not even exhibit any symptoms. Women, older persons, and those with diabetes may also experience symptoms that differ from or are less prevalent than those listed above. For routine health examinations and screenings, it is therefore always a good idea to see a heart expert.
In Conclusion
People can reduce their risk of blood clots and improve their general health and well-being by embracing healthy behaviors and getting help from a heart disease specialist.. Dr. Ravinder Singh Rao is a renowned cardiologist in Jaipur, Rajasthan, and one of the best-known TAVR experts in India.